Cells and Cell Types
By default, cells in the sheet are edit cells. You can choose to designate cells to be one of 15 available types as described in the following table.
| Cell Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Button | Displays a button (The button cell can contain text, graphics, or both.) |
| Check Box | Displays a check box |
| Combo Box | Displays a combo box and provides a list of items for display in the combo box |
| Currency | Displays or allows editing of a formatted currency value |
| Custom | Displays a custom cell |
| Date | Displays or allows editing of formatted dates |
| Edit | Displays or allows editing of text |
| Number | Displays or allows editing of a formatted numeric value |
| Owner-Drawn | Displays a user-defined cell type |
| Percent | Displays or allows editing of a formatted percent value |
| PIC | Displays or allows editing of a formatted PIC (mask) |
| Picture | Displays a picture |
| Scientific | Displays or allows editing of a numeric value in scientific notation |
| Static Text | Displays non-editable, non-scrolling text |
| Time | Displays or allows editing of a formatted time value |
Each cell type presents special characteristics that you can customize for your needs. For example, you can specify maximum and minimum values, a separator character, and a format for date cells.
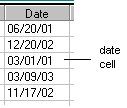
The following figure illustrates date cells that have the format MM/DD/YY and that have a slash character as a separator.
For more information about selecting a cell type for a cell, see Setting the Cell Type.
Individual cells can display specialized borders and background and foreground colors. You can align text in a cell, and in addition, cells can display text as overflowing into adjacent cells, if you prefer. For more information about customizing cell appearance and cell text, see Customizing Cell Borders, Allowing Cells to Overflow, and the descriptions for customizing cell types in Setting the Cell Type.
You can prevent users from interacting with a cell by locking the cell. For more information, see Locking Cells.
Cells can span other cells, or they can merge automatically if they contain the same content. For more information about spanning and merging, see Spanning Cells and Merging Cells.