In order to work with formula text box in a spreadsheet, refer to the following tasks.
- Setting up the Formula Text Box
- Using the Formula Text Box
- Using Intersect Formula and Mixed Reference Formula
Setting up the Formula Text Box
You can set up a floating formula bar that can be used to add formulas. The formula bar is similar to the formula editor available to the developer and has the appearance of a text box. The formula bar not only renders a list of calculation functions but also provides a visual method of selecting cell ranges for the formula.
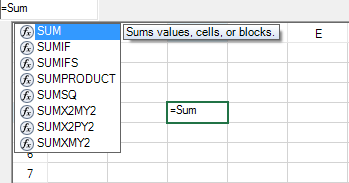
In order to set up the formula bar at run time, you can use the FormulaTextBox class. You can also draw the formula text box on the form and assign it to Spread at design time. Select the formula text box icon in the Toolbox and drag it to the form. Select the formula text box verb and attach it to Spread.
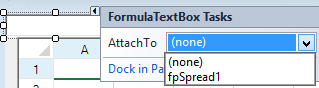
The AllowUserFormulas property allows the user to type formulas in the cell in the Spread control.
If you set the AllowUserFormulas property to True, then the formulas that are typed in a cell will show up in the formula bar.
Using the Formula Text Box
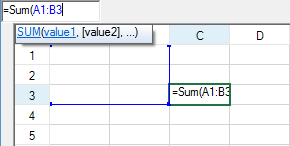
To use the formula text box, type the equal sign (=) and then start typing the name of the formula. This brings up a list of functions that start with that letter. You can then type the left parenthesis and either select a block of cells by dragging the mouse over that range or type cell values by absolute or relative reference. The figure below shows the selection of a range of cells from A1 to B3.
Using Code
Create the formula editor and attach it to the control.
Example
This example code creates the floating formula bar.
| C# |
Copy Code
|
|---|---|
FarPoint.Win.Spread.FormulaTextBox editor = new FarPoint.Win.Spread.FormulaTextBox(); editor.Location = new Point(0, 0); editor.Size = new Size(80, 20); this.Controls.Add(editor); editor.Attach(fpSpread1); // This line will disconnect the formula bar from the control // editor.Detach(); |
|
| VB |
Copy Code
|
|---|---|
Dim editor As New FarPoint.Win.Spread.FormulaTextBox editor.Location = New Point(0, 0) editor.Size = New Size(80, 20) Controls.Add(editor) editor.Attach(fpSpread1) ‘ This line will disconnect the formula bar from the control ‘ editor.Detach() |
|
Using Intersect Formula and Mixed Reference Formula
You can use the intersect formula and the mixed reference formula while working with formula text box in the spreadsheets.
In order to create an intersect formula in a worksheet, users need to select or provide two cell ranges separated by spaces as parameters of the calculation function that is being used.
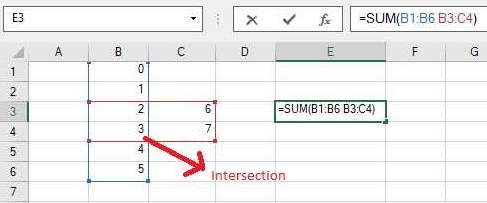
An example screenshot shared below depicts the intersection formula used in a formula text box for SUM function containing two cell ranges - B1:B6 and B3:C4 separated by the space character. When the formula is calculated, it returns the evaluated sum of all the values appearing in the intersection area (an area where rows and columns intersect as highlighted in the image) of the two cell ranges.
A mixed reference formula refers to the combination of relative and absolute cell references (absolute column and relative row or absolute row and relative column) used in a worksheet. The absolute cell references are also known as fixed references and are represented by the cells with the dollar symbol ($) placed in front of them. The relative cell references change when the formula is dragged or copied across rows and columns in the worksheet.
For more information on formulas, refer to Managing Formulas in Cells and the Formula Reference.
Using Code
You can use the intersect formula and the mixed reference formula in the formula text box in the spreadsheet.
Example
This example code shows how to work with intersect formula and mixed reference formula in the spreadsheet.
| C# |
Copy Code
|
|---|---|
// Using intersect formula fpSpread1.Sheets[0].Cells[0, 1].Value = 0; fpSpread1.Sheets[0].Cells[1, 1].Value = 1; fpSpread1.Sheets[0].Cells[2, 1].Value = 2; fpSpread1.Sheets[0].Cells[3, 1].Value = 3; fpSpread1.Sheets[0].Cells[4, 1].Value = 4; fpSpread1.Sheets[0].Cells[5, 1].Value = 5; fpSpread1.Sheets[0].Cells[2, 2].Value = 6; fpSpread1.Sheets[0].Cells[3, 2].Value = 7; fpSpread1.Sheets[0].Cells[2, 4].Formula = "SUM(B1:B6 B3:C4)"; // Using mixed reference formula fpSpread1.Sheets[0].Cells[5, 5].Formula = "SUM($B1, $B$2, B$3, B4)"; |
|
| VB |
Copy Code
|
|---|---|
'Using intersect formula fpSpread1.Sheets(0).Cells(0, 1).Value = 0 fpSpread1.Sheets(0).Cells(1, 1).Value = 1 fpSpread1.Sheets(0).Cells(2, 1).Value = 2 fpSpread1.Sheets(0).Cells(3, 1).Value = 3 fpSpread1.Sheets(0).Cells(4, 1).Value = 4 fpSpread1.Sheets(0).Cells(5, 1).Value = 5 fpSpread1.Sheets(0).Cells(2, 2).Value = 6 fpSpread1.Sheets(0).Cells(3, 2).Value = 7 fpSpread1.Sheets(0).Cells(2, 4).Formula = "SUM(B1:B6 B3:C4) 'Using mixed reference formula fpSpread1.Sheets(0).Cells(5, 5).Formula = "SUM($B1, $B$2, B$3, B4)" |
|